
IgG Proteases for Gene Therapy Applications
The development and successful commercialization of gene therapy technologies as new treatments have spurred great interest and investments in this field of research. Many challenges remain to be solved to establish gene therapy as a mainstream line of treatment, but there are currently many promising and life-changing gene therapy programs in preclinical and clinical development. Preexisting antibodies against the capsid of adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors is a major challenge for many gene therapies that could block uptake and limit the transduction of the new genetic material. The anti-AAV antibodies are prevalent both in humans and preclinical disease models. In patient populations, up to 50% of the patients could be excluded from treatment due to high titers of anti-AAV antibodies. Several strategies are explored to reduce the antibody response, once such is enzymatic pretreatment using IgG-specific proteases.
IdeS is an IgG-specific cysteine protease that rapidly digests IgG to F(ab’)2 and Fc/2 fragments (Pawel-Rammingen et al., 2002). This unique enzyme has a broad range of applications for analysis of therapeutic antibodies, and is also explored as a therapeutic agent for treatment of antibody-mediated disease (Sjögren et al., 2016, Winstedt et al., 2015). IdeS was discovered and characterized from Streptococcus pyogenes, and similar proteases such as IdeZ has been discovered in other streptococcal species.
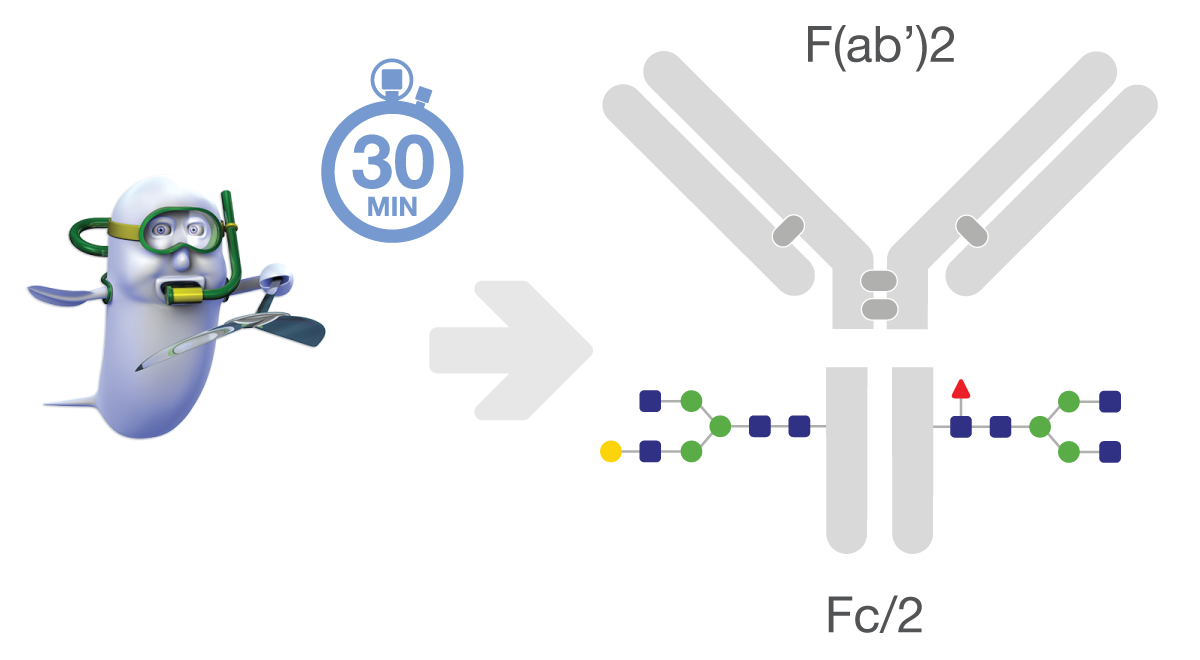
The IdeS enzyme has been explored in gene therapy applications and has been shown to increase the transduction of genetic material in non-human primates with preexisting anti-AAV antibodies (Leborgne et al., 2020). In the study published in Nature Medicine, the scientists injected 0.5 mg/kg of IdeS at two days prior to gene therapy and they observed both digested anti-AAV antibodies and a significant increase in vector genome copy number in liver cells. In a similar study, a single dose of 0.5 mg/kg of IdeZ was sufficient to rescue AAV transduction in macaques as well as in mice with human antibodies (Elmore et al., 2020).
Genovis provides a range of IgG proteases where FabRICATOR (IdeS) and FabRICATOR Z (IdeZ) are provided for research use and are available in highly purified low endotoxin formats compatible with preclinical requirements. Additionally, Genovis provides Anti-FabRICATOR (anti-IdeS) antibodies of a species that is resistant to digestion and allow researchers to develop affinity-based methods to monitor the IdeS enzyme during preclinical research.

FabRICATOR, Anti-FabRICATOR and FabRICATOR Z.
Reference Highlights
Elmore, Z.C. et al., 2020. Rescuing AAV gene transfer from neutralizing antibodies with an IgG-degrading enzyme. JCI insight, 5(19).
Leborgne, C. et al., 2020. IgG-cleaving endopeptidase enables in vivo gene therapy in the presence of anti-AAV neutralizing antibodies. Nature Medicine, pp.1–20.
Pawel-Rammingen, von, U., Johansson, B.P. & Björck, L., 2002. IdeS, a novel streptococcal cysteine proteinase with unique specificity for immunoglobulin G. The EMBO journal, 21(7), pp.1607–1615.
Sjögren, J., Olsson, F. & Beck, A., 2016. Rapid and improved characterization of therapeutic antibodies and antibody related products using IdeS digestion and subunit analysis. The Analyst, 141(11), pp.3114–3125.
Winstedt, L. et al., 2015. Complete removal of extracellular IgG antibodies in a randomized dose-escalation phase I study with the bacterial enzyme IdeS – a novel therapeutic opportunity. PloS one, 10(7), p.e0132011.
